前言
开始之前,举一个使用spring boot启动web应用的代码示例:
1 |
|
通过上述代码可以看到,Spring Boot 中应用启动的核心入口在SpringApplication 这个类中完成。
继续查看在SpringApplication的run方法内部执行中,主要分为两步:1.初始化创建一个SpringApplication,2.然后执行run(String... args)方法对Application进行启动。
1 | public staticConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class[] primarySources, String[] args) { |
由此,本文对spring boot启动过程的分析也会从这两部分进行展开。1)SpringApplication的初始化部分; 2)SpringApplication的run执行部分。
SpringApplication的初始化
SpringApplication类私有变量
下边的图简单描述了SpringApplication类所包含的一些私有变量。后续会结合类的构造函数来分析其中的重要私有变量及其左右。

SpringApplication构造函数
结合Class的构造函数来重点看一下下面几个变量的作用以及如何进行初始化的。
1 | public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) { |
ResourceLoader
表示Spring中用来加载资源的资源加载器。
webApplicationType
代表这个SpringApplication的类型,主要包括三个类型:NONE / SERVLET / REACTIVE
NONE: The application should not run as a web application and should not start an embedded web server.
SERVLET: The application should run as a servlet-based web application and should start anembedded servlet
web server.
REACTIVE: The application should run as a reactive web application and should start anembedded reactive web server.
SpringBoot是怎么知道究竟是那种类型的ApplicationType的呢?实现的代码在方法deduceWebApplicationType()中。
1 | private WebApplicationType deduceWebApplicationType() { |
在这段代码里一个核心的方法调用是 ClassUtils.isPresent(String className,@NullableClassLoader classLoader),这个方法是判断参数中的className是否存在并可以加载成功。由此可见WebApplicationType类型的判断取决于引入的jar包。其中,
REACTIVE_WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASS 对应的类为 _org.springframework.web.reactive.DispatcherHandler_,对应的package是spring-webflux
MVC_WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASS 对应的类为org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet , 对应的package是 spring-webmvc
WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASSES 对应的类为{“javax.servlet.Servlet”,”org.springframework.web.context.ConfigurableWebApplicationContext”},对应的package是servlet-api和spring-web
ApplicationContextInitializer
用来在对ApplicationContext进行refresh操作之前对Application context进行一些初始化操作。
Callback interface for initializing a Spring {@ConfigurableApplicationContext} prior to being
{@ConfigurableApplicationContext#refresh()} refreshed.
Typically used within web applications that require some programmatic initialization of the application context.
For example, registering property sources or activating profiles against the
{@ConfigurableApplicationContext#getEnvironment()}
context’s environment. See {@ContextLoader} and {@FrameworkServlet} support for declaring a “contextInitializerClasses” context-param and init-param, respectively.
通过查看代码,我们可以看到ApplicationContextInitializer的获取是通过调用 getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type)方法得到的,这个方法实际是去寻找指定Class类型的类并将其实例化返回。那具体是从哪里找呢? 会在后边的小节单独分析一下
ApplicationListener
基于观察者模式的Application的事件监听器。将ApplicationListener注册到ApplicationContext中,当有对应事件发生时,监听器会被调用
Interface to be implemented by application event listeners.
Based on the standard {@java.util.EventListener} interface for the Observer design pattern.
As of Spring 3.0, an ApplicationListener can generically declare the event type that it is interested in. When
registered with a Spring ApplicationContext, events will be filtered accordingly, with the listener getting invoked for matching event objects only.
与获取ApplicationContextInitializer的过程一直, ApplicationListener的获取也是通过调用getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type)实现。
mainApplicationClass
启动应用程序的main class.通过分析当前的程序堆栈信息获取。
1 | private Class<?> deduceMainApplicationClass() { |
关于getSpringFactoriesInstances
ee
SpringApplication的run
整体流程
run方法是SpringApplication的核心方法,在这个方法内部完成了 系统属性的注入,Runner的执行,创建、准备以及refresh整个ApplicationContext 核心流程。大致可以将整个run方法归纳分解成6个步骤。

细节分析
下边对这六个步骤进行详细的分析和解读。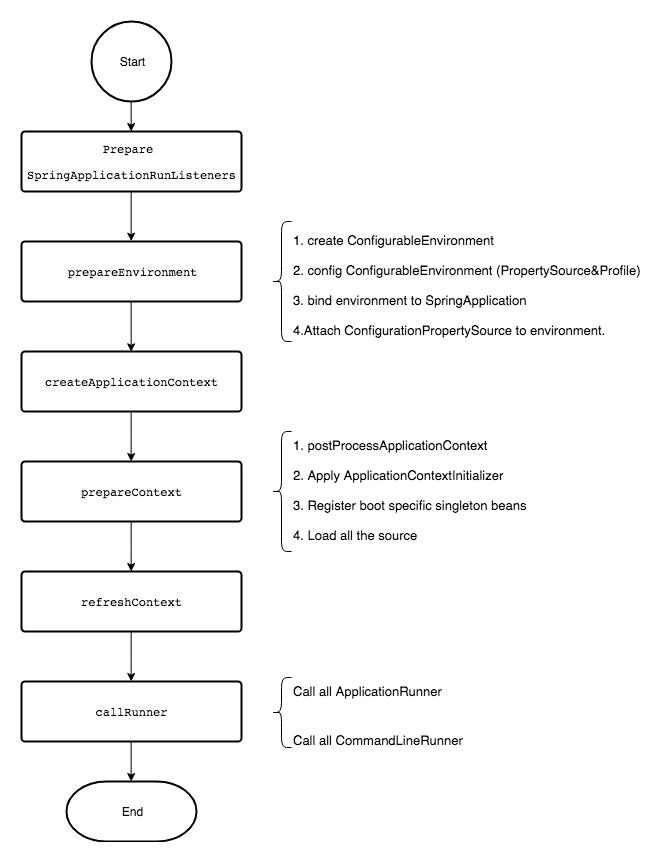
SpringApplicationRunListeners
SpringApplicationRunListener是事件监听器,用来监听SpringApplication的启动过程,监听到事件发生时进行一些回调操作。通过下边的代码可以看到获取的核心方法是getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringApplicationRunListener.class, types,
this, args)完成的。
1 | private SpringApplicationRunListeners getRunListeners(String[] args) { |
Prepare Environment
配置Application的环境,主要是一些property,这些属性会在创建ApplicationContext以及Referesh的时候起到左右。
1 | private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment( |
核心流程:
创建一个
ConfigurableEnvironment配置
ConfigurableEnvironment,主要配置PropertySource(包括defaultProperties和addCommandLineProperties)和Profile。将environment绑定至
SpringApplicationAttach一个
ConfigurationPropertySource至environment.
Create ApplicationContext
根据this.webApplicationType的类型来创建不同的ConfigurableApplicationContext。
1 | protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() { |
Prepare Context
在 prepareContext的过程中,首先会运行一些初始化的流程,然后会注册一些spring boot启动所需要的bean,加载一些初始的beans。
1 | //1. Apply any relevant post processing the ApplicationContext |
Refresh Context
对前边两步中创建和准备好的application context执行refresh操作,这一部分的具体实现在spring-context包中。本文不再具体分析。
Call Runner
主要是调用一下设置的一些ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner。
1 | private void callRunners(ApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) { |
总结
Spring boot实际上是对原有Spring Application启动方式的一种革命。在传统的Spring Application中,程序启动的方式是传统的web容器(如tomcat、jetty)为入口,spring application作为webAppContext插入到web容器中。而在spring boot的方式中,完全是以spring application为主,传统的web容器作为插件嵌入到spring application中。
